What Is The Function Of Main Distribution Board?
22nd Mar 2025
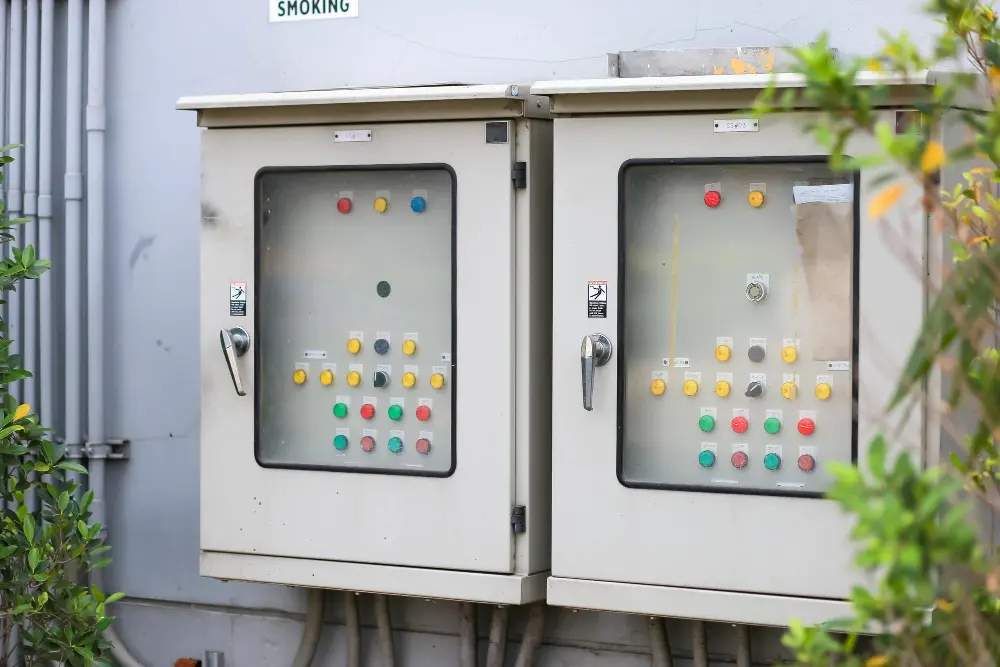
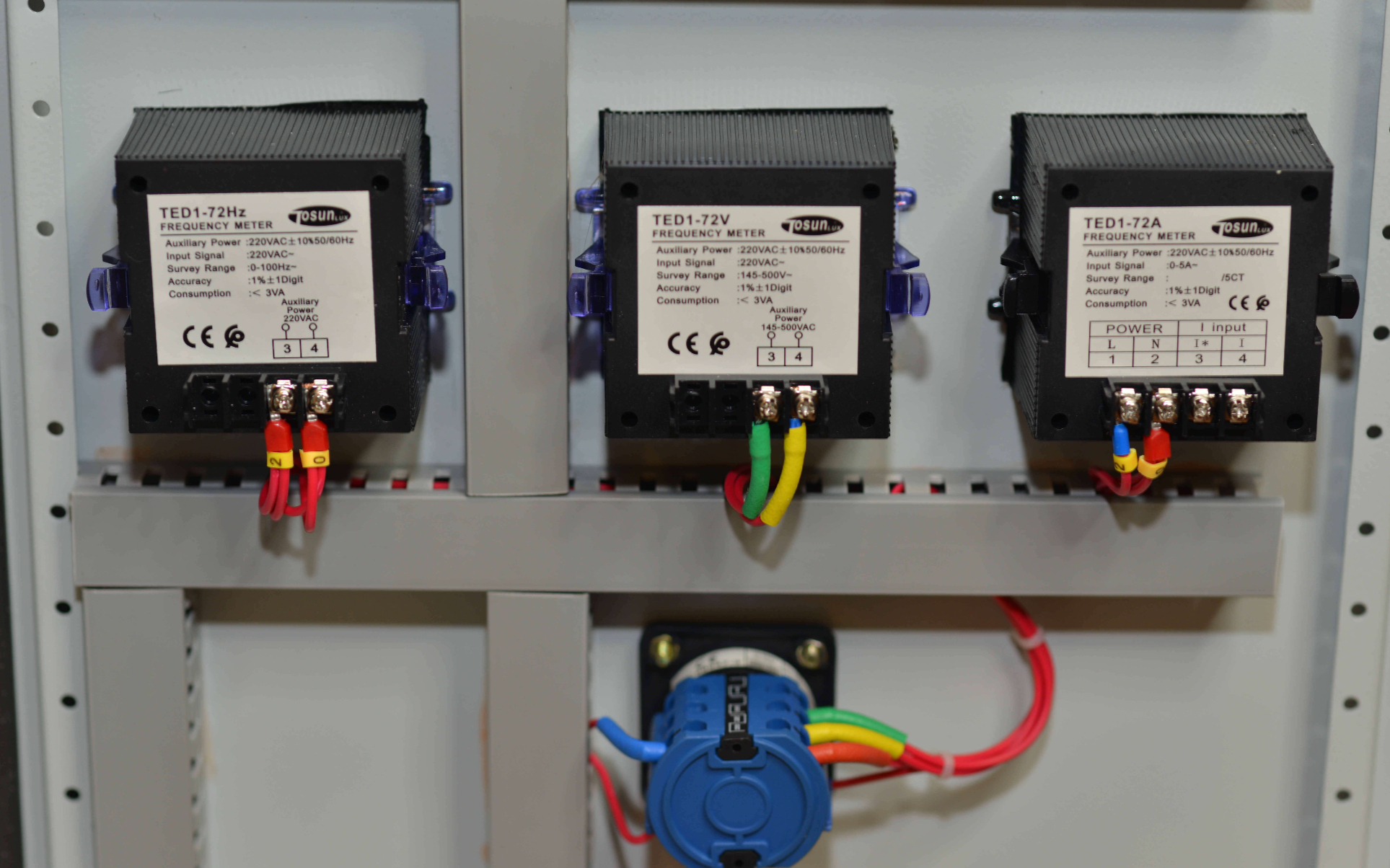
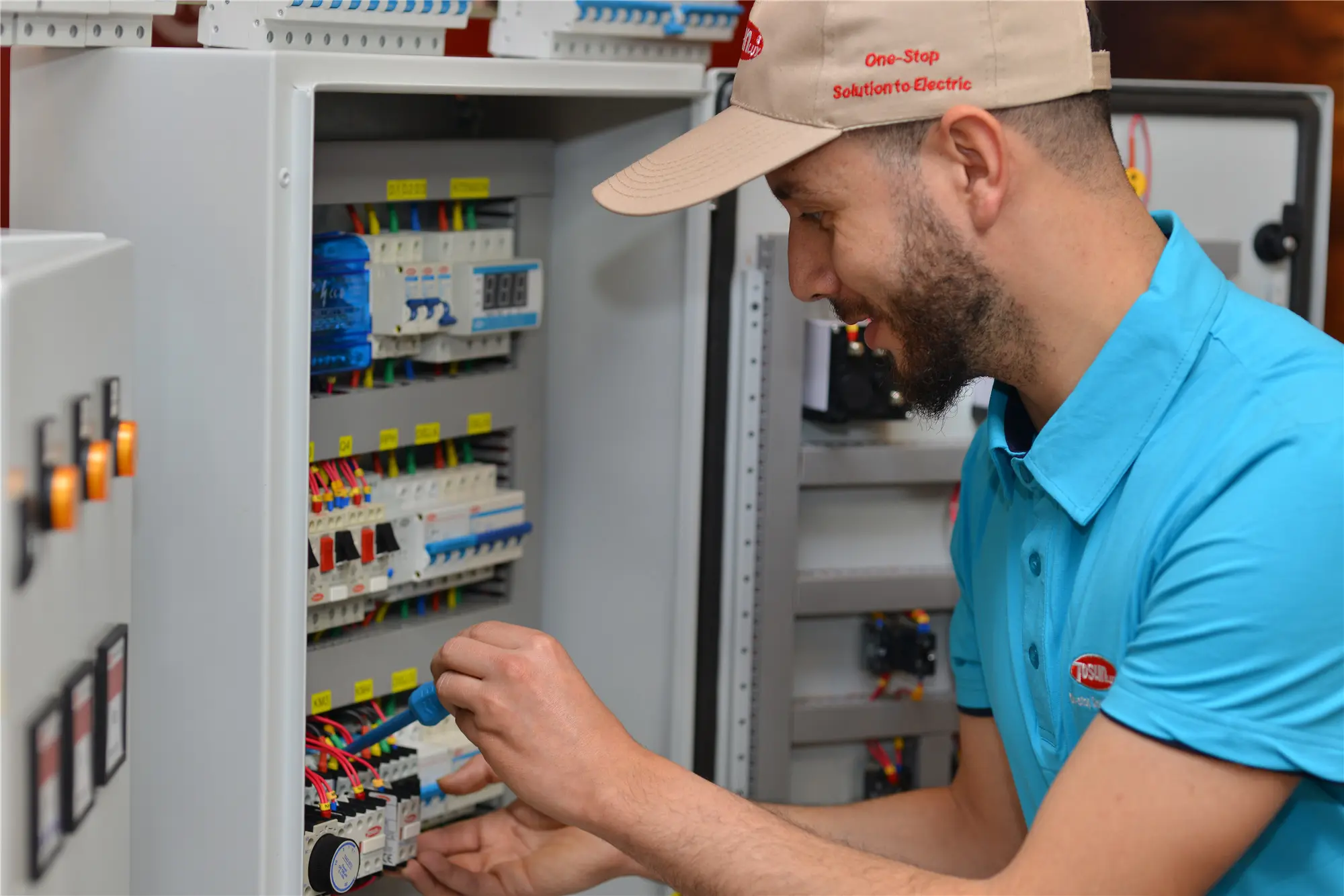
Did you know that distribution boards are key to safely distributing electrical power in over 90% of homes and businesses, playing a crucial role in electrical distribution? These boards control electrical circuits, preventing faults and fires. In this article, we’ll explain what main distribution boards are, how they differ from sub distribution boards, and their role in safety. We’ll cover important parts like circuit breakers that stop overloads and short circuits. By the end, you’ll see how distribution boards keep electrical systems running smoothly. This easy-to-read guide is packed with data and expert tips to help you understand these important systems. The Main Function Of The Electrical Distribution Box The main function of a distribution box is to manage and distribute electrical power safely and efficiently throughout a building. Here’s a simple breakdown: Power Distribution: It receives power from the main supply or main power supply and distributes it to various circuits within a structure, ensuring that each part of the building gets the necessary electrical energy. Safety and Protection: The distribution box houses circuit breakers and other protective devices that prevent electrical faults and electrical hazards, such as overloads and short circuits, which can cause electrical fires. Control and Management: It allows for easy control over the electrical circuits or electrical circuits, making it convenient to perform maintenance or repairs by isolating specific areas without disrupting the entire electrical system. Centralized Monitoring: With all switches and meters in one place, it provides a centralized point for monitoring the electrical load or electrical loads and […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά