Voltage Protector vs. Surge Protector: Which One Do You Really Need?
03rd Jul 2025
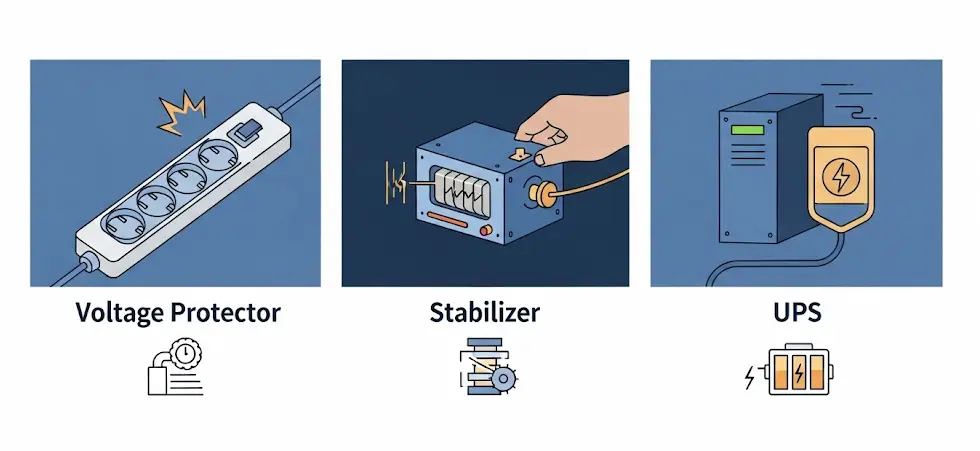
Alt-text: Technician monitoring control systems in an industrial power facility When choosing between a voltage protector vs surge protector, it can feel confusing. Both claim to defend your equipment, but they tackle two distinct electrical threats: sudden spikes vs. ongoing voltage swings. This surge protector vs voltage protector breakdown will help you clearly understand what each one does—and when you need both. Hero Product Highlight electrical supply wholesaler Discover a full range of electrical products from a trusted electrical supply wholesaler. TOSUNlux offers circuit breakers, contactors, switches, and more for global markets. View Product What a Surge Protector Does A surge protector is like a bouncer for your devices. It stands guard at the outlet, ready to absorb or divert sudden voltage spikes—those brief surges caused by lightning, grid switching, or large appliances switching on or off. These spikes can reach thousands of volts in mere microseconds, damaging circuit boards today and degrading them tomorrow. Hero Product Highlight TSP8 Surge Protector TSP8 Surge Protector by TOSUNlux offers fast, reliable protection against lightning and overvoltage for your electrical systems. View Product Key specs: Most offices should install strip-style surge protectors and consider a whole-building surge device at the main panel for deeper protection. What a Voltage Protector (Regulator/Stabilizer) Does A voltage protector, also known as a voltage regulator or stabilizer, monitors and adjusts the voltage over time. It safeguards against sustained under-voltage (brownouts) or over-voltage that can shorten equipment life, cause errors, or trigger shutdowns. This is vital in regions with an unstable supply. Models range […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά