Transient Voltage Protection Strategies for Data Centers and IT Racks
07th Jul 2025
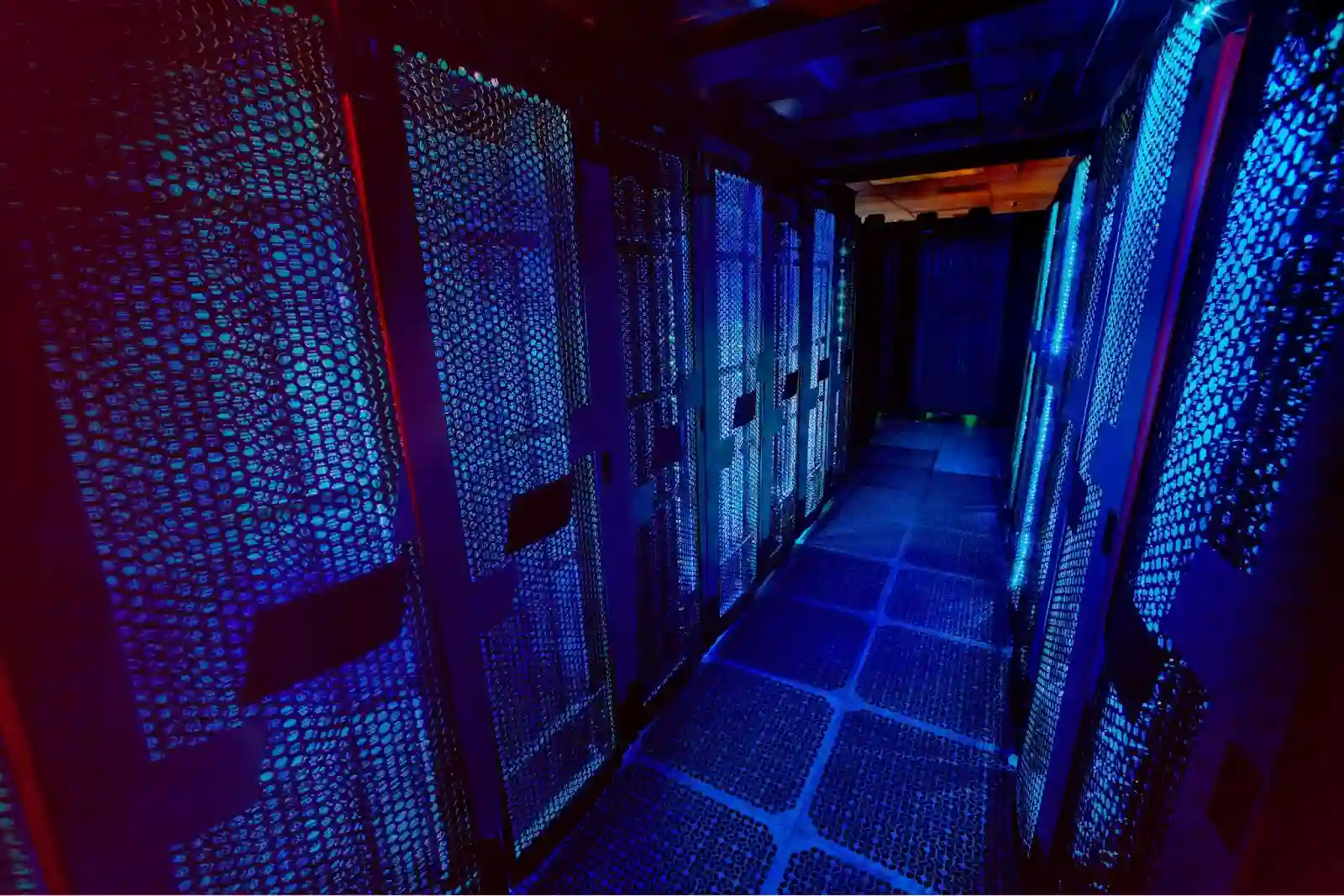
Alt-text: Server racks in a modern data center with controlled lighting and secure enclosures In modern data centers, transient voltage surge protector (TVSS) devices are vital for safeguarding sensitive equipment. These short, unexpected voltage spikes—often caused by lightning, switching events, or generator transfers—can corrupt data or damage servers in microseconds. TOSUNlux provides high-performance Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) that enable a full, end-to-end power protection strategy from a single trusted manufacturer—ideal for IT racks, server rooms, and overall data center environments. Understanding Transient Voltage Protection Transient voltage surge protectors detect voltage spikes and instantly shunt them away via MOVs, TVS diodes, or gas discharge tubes, clamping energy before it reaches your equipment . They typically react in nanoseconds—fast enough to shield high-speed data electronics. Key protection points include: Layered SPD placement ensures every potential entry point for transient surges is covered. Power Conditioner Surge Protector and Voltage Regulator A power conditioner combines surge protection with voltage regulation and line noise filtering. It smooths out brownouts, spikes, and electrical interference while delivering clean, stable power. A well-designed power conditioner surge protector and voltage regulator keeps output voltage within safe ranges, suppresses surges, and filters out electrical noise. This is especially useful in racks running sensitive servers or switching hardware where both voltage consistency and surge protection matter. DC Voltage Surge Protector Many IT systems use DC power—especially telecom racks and PoE networks. A DC voltage surge protector safeguards these circuits from transient spikes. Components like TVS diodes, rated to clamp in under 1 ps, guard against fast spikes […]
Read More : +86-139 0587 7291
: +86-139 0587 7291 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français العربية
العربية Português do Brasil
Português do Brasil Українська
Українська Türkçe
Türkçe Polski
Polski Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia हिन्दी
हिन्दी اردو
اردو አማርኛ
አማርኛ Հայերեն
Հայերեն ไทย
ไทย Монгол
Монгол فارسی
فارسی Shqip
Shqip Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά